Modern businesses face a critical choice when selecting monitoring solutions. Should they stick with traditional monitoring systems or embrace telemetry technology? This decision impacts everything from operational efficiency to cost management. Understanding the differences between these approaches helps organizations make informed choices.
Understanding Traditional Monitoring Systems
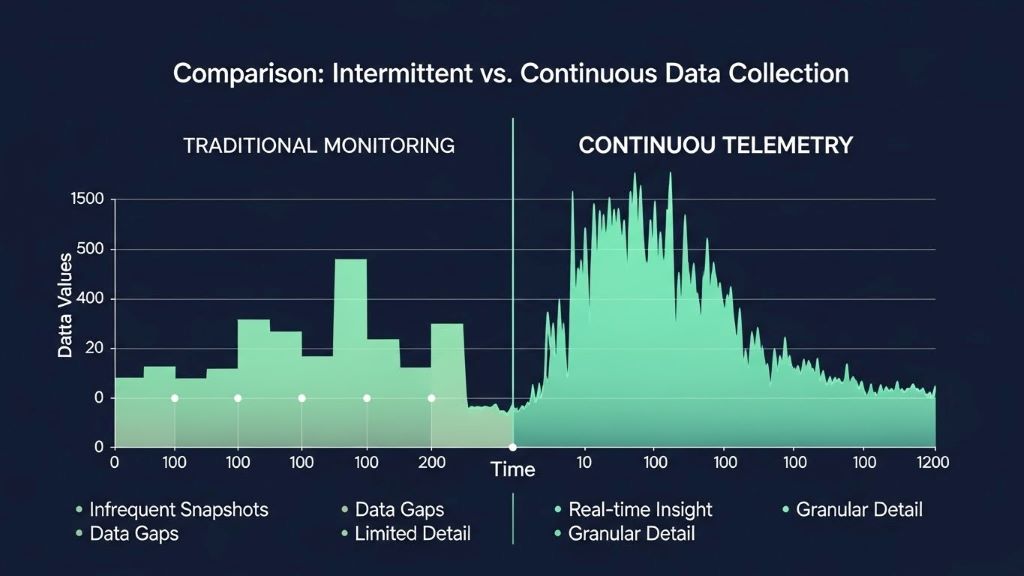
Traditional monitoring systems have served businesses for decades. These systems typically operate on fixed intervals, checking specific parameters at scheduled times. They collect data from predetermined points and send alerts when values exceed set thresholds.
Most traditional systems use simple alert mechanisms. When a metric crosses a threshold, the system triggers a notification. This approach works well for basic monitoring needs. However, it offers limited insight into complex system behaviors.
Traditional monitoring often requires manual configuration. IT teams must define what to monitor, set thresholds, and establish alert rules. This process demands significant upfront investment in planning and setup. Additionally, scaling these systems across multiple locations or departments can become challenging.
What Is Telemetry Technology?
Telemetry technology represents a modern approach to data collection and analysis. The term comes from Greek words meaning “remote measurement.” Unlike traditional systems, telemetry continuously streams data from various sources in real time.
This technology automatically collects vast amounts of detailed information. It captures not just whether something is working but how it is working. Telemetry systems track performance metrics, user behaviors, system health indicators, and environmental conditions simultaneously.
According to IBM’s research on telemetry systems, modern telemetry can process millions of data points per second. This capability enables organizations to gain unprecedented visibility into their operations.
Key Differences in Data Collection
The data collection methods differ significantly between these two approaches. Traditional monitoring systems sample data at intervals. They might check server status every five minutes or temperature readings every hour. This periodic sampling can miss important events that occur between checks.
Conversely, telemetry systems collect data continuously. They capture every transaction, every user interaction, and every system state change. This comprehensive approach ensures nothing falls through the cracks.
Traditional systems typically focus on infrastructure metrics. They monitor server uptime, network bandwidth, and hardware health. Telemetry goes further by tracking application performance, user experience metrics, and business-level indicators.
Analysis and Insights
Traditional monitoring excels at detecting known problems. When metrics exceed predefined thresholds, alerts trigger immediately. This reactive approach works well for straightforward issues. However, it struggles with complex problems that involve multiple interrelated factors.
Telemetry systems leverage advanced analytics and machine learning. They identify patterns humans might miss and predict potential issues before they occur. This proactive capability transforms monitoring from reactive firefighting to preventive maintenance.
Furthermore, telemetry provides context that traditional systems lack. Instead of simply knowing a server is slow, telemetry reveals which applications are affected, which users are impacted, and what conditions led to the slowdown.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scaling traditional monitoring systems requires significant effort. Adding new servers, applications, or locations means manually configuring additional monitoring points. Each new component needs its own rules, thresholds, and alert configurations.
Telemetry systems scale more naturally. They automatically discover new components and begin collecting relevant data. This self-service approach reduces administrative overhead and speeds up deployment.
Additionally, telemetry adapts to changing environments more effectively. As applications evolve or new technologies enter the infrastructure, telemetry systems adjust their data collection accordingly. Traditional systems require manual updates to accommodate such changes.
Cost Considerations
Initial costs for traditional monitoring systems are often lower. The technology is mature, widely available, and well understood. Many open-source options exist for organizations with limited budgets.
However, hidden costs accumulate over time. Manual configuration demands skilled personnel. Scaling requires additional hardware and software licenses. Maintaining multiple point solutions for different monitoring needs increases complexity and expense.
Telemetry technology typically requires higher upfront investment. The infrastructure for handling massive data streams costs more initially. Nevertheless, long-term costs may be lower due to automation, reduced manual intervention, and consolidated monitoring capabilities.
Real-Time Visibility
Traditional monitoring provides snapshots of system health. These periodic checks offer reasonable visibility for stable environments with predictable workloads. Organizations can identify problems within minutes of their occurrence.
Telemetry delivers genuine real-time visibility. Every event is captured as it happens. This immediate awareness enables faster response times and minimizes the impact of incidents. Teams can see problems developing and take corrective action before users are affected.
Real-time data also enables dynamic decision-making. Organizations can adjust resources, reroute traffic, or modify configurations based on current conditions rather than historical patterns.
Integration Capabilities
Traditional monitoring systems often operate in silos. Each tool monitors its specific domain with limited communication between systems. Correlating information across different monitoring solutions requires manual effort.
Modern telemetry platforms emphasize integration. They collect data from diverse sources into unified dashboards. This holistic view makes it easier to understand how different systems interact and affect each other.
According to Gartner’s analysis of monitoring trends, integrated observability platforms are becoming essential for managing complex digital environments. Telemetry technology aligns perfectly with this trend.
Use Cases and Applications
Traditional monitoring suits straightforward environments with stable configurations. Small businesses with limited IT infrastructure often find traditional systems adequate. Manufacturing facilities with fixed equipment also benefit from this approach.
Telemetry technology shines in dynamic, complex environments. Cloud-native applications, microservices architectures, and distributed systems generate data volumes that overwhelm traditional monitoring. E-commerce platforms, financial services, and SaaS providers typically require telemetry capabilities.
Moreover, telemetry enables advanced use cases like customer experience monitoring, performance optimization, and predictive maintenance. These applications require the comprehensive data collection that only telemetry provides.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting between these technologies depends on specific organizational needs. Consider your infrastructure complexity, growth plans, and monitoring requirements. Small, stable environments may not need telemetry’s advanced capabilities.
However, most modern organizations benefit from telemetry technology. The digital landscape grows increasingly complex. Applications span multiple clouds, edge locations, and on-premises data centers. User expectations for performance and reliability continue rising.
Therefore, even organizations currently satisfied with traditional monitoring should plan for eventual telemetry adoption. The transition doesn’t need to happen overnight. Many companies implement hybrid approaches, maintaining traditional monitoring while gradually introducing telemetry capabilities.
Conclusion
Traditional monitoring systems and telemetry technology serve different purposes in today’s IT landscape. Traditional systems offer simplicity and lower initial costs but provide limited visibility and require significant manual effort. Telemetry technology delivers comprehensive real-time insights, advanced analytics, and better scalability at the cost of higher initial investment.
The best choice depends on your organization’s specific needs, infrastructure complexity, and growth trajectory. As digital environments become more sophisticated, telemetry technology increasingly represents the future of monitoring. Organizations should evaluate their current requirements while planning for tomorrow’s challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main advantage of telemetry over traditional monitoring?
Telemetry provides continuous, real-time data collection with comprehensive coverage of all system components. Unlike traditional monitoring’s periodic sampling, telemetry captures every event and transaction, enabling better problem detection and faster response times.
Can small businesses benefit from telemetry technology?
Yes, although traditional monitoring may suffice for very small operations. As businesses grow or adopt cloud services, telemetry becomes increasingly valuable. Many vendors offer scaled solutions suitable for organizations of various sizes.
Is it possible to use both systems together?
Absolutely. Many organizations implement hybrid approaches, maintaining traditional monitoring for stable legacy systems while deploying telemetry for modern applications and infrastructure. This strategy provides comprehensive coverage during transition periods.
How much data does telemetry technology generate?
Telemetry systems can generate enormous data volumes, potentially millions of data points per second in large environments. Modern platforms include data management features like compression, aggregation, and intelligent sampling to make storage and analysis manageable.
What skills do teams need to manage telemetry systems?
Teams need understanding of data analysis, modern application architectures, and cloud technologies. However, many telemetry platforms offer user-friendly interfaces that reduce the learning curve. Training resources and vendor support help teams develop necessary competencies.
Related Topics: